Query Matching Guide
Learn how to percolate lucene Queries to generate custom events based on business policies This guide covers:
-
lucene syntax
-
matching queries
1. Prerequisites
To complete this guide, you need:
-
less than 15 minutes
-
an IDE
-
JDK 1.8+ installed with
JAVA_HOMEconfigured appropriately -
Apache Maven 3.5.3+
-
The completed greeter application from the Event Aggregation Guide
2. Architecture
In this guide, we expand on the initial stream that was created as part of the Event Aggregation Guide. We cover how to raise custom alerts based on lucene matching query criterion.
3. Solution
We recommend that you follow the instructions in the next sections and create the application step by step. However, you can go right to the completed example.
-
Clone the Git repository:
git clone https://github.com/hurence/logisland-quickstarts.git, or download an archive. -
The solution is located in the
conf/core/match-queries.ymlfile. -
This guide assumes you already have the completed application from the
event-aggregationguide.
4. Logisland job setup
Our application will add a new feature to the previous app (Event Aggregation Guide) to match again some particuliar criterion. This is the heart of the complex event processing as you can define your own logic to build some new information over your data.
-
First stream converts apache logs to typed records (please note the use of
ConvertFieldsTypeprocessor) -
Second the sql stream we will compute every x seconds, the top twenty
src_ipfor connections count as newtop_client_metricsRecord containingconnections_countandavg_bytes_outfields. -
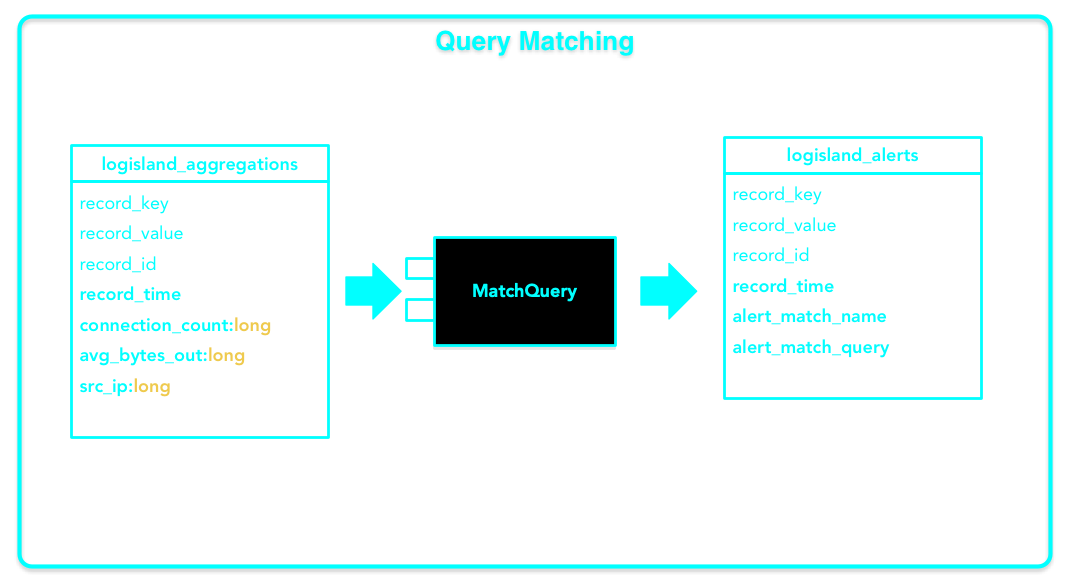
Third stream creates alerts records within the
MatchQueryprocessor which matches incomming records (fromlogisland_aggregations) against some criteria to eventualy produce some alerts to send them tologisland_alerts
# match threshold queries
- stream: aggregation_threshold_matching_stream
component: com.hurence.logisland.stream.spark.KafkaRecordStreamParallelProcessing
configuration:
kafka.input.topics: logisland_aggregations
kafka.output.topics: logisland_alerts
kafka.input.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.JsonSerializer
kafka.output.topics.serializer: com.hurence.logisland.serializer.JsonSerializer
processorConfigurations:
# a parser that produce alerts from lucene queries
- processor: match_query
component: com.hurence.logisland.processor.MatchQuery
configuration:
numeric.fields: bytes_out,connections_count
too_much_bandwidth: avg_bytes_out:[25000 TO 5000000]
too_many_connections: connections_count:[150 TO 300]
output.record.type: threshold_alertIn this stream for example a new record of type too_much_bandwidth would be created if one record match the condition avg_bytes_out:[25000 TO 5000000]. Please read the the following paragraph on Lucene Query Syntax to learn more.
5. Lucene Query Syntax
Here are some query examples demonstrating the query syntax.
Keyword matching
-
Search for word "foo" in the title field :
title:foo -
Search for phrase "foo bar" in the title field :
title:"foo bar" -
Search for phrase "foo bar" in the title field AND the phrase "quick fox" in the body field :
title:"foo bar" AND body:"quick fox" -
Search for either the phrase "foo bar" in the title field AND the phrase "quick fox" in the body field, or the word "fox" in the title field :
(title:"foo bar" AND body:"quick fox") OR title:fox -
Search for word "foo" and not "bar" in the title field :
title:foo -title:bar
Wildcard matching
-
Search for any word that starts with "foo" in the title field :
title:foo* -
Search for any word that starts with "foo" and ends with bar in the title field :
title:foo*bar
Note that Lucene doesn’t support using a * symbol as the first character of a search.
Proximity matching
Lucene supports finding words are a within a specific distance away.
-
Search for "foo bar" within 4 words from each other :
"foo bar"~4
Note that for proximity searches, exact matches are proximity zero, and word transpositions (bar foo) are proximity 1.
A query such as "foo bar"~10000000 is an interesting alternative to foo AND bar.
Whilst both queries are effectively equivalent with respect to the documents that are returned, the proximity query assigns a higher score to documents for which the terms foo and bar are closer together.
Range searches
Range Queries allow one to match documents whose field(s) values are between the lower and upper bound specified by the Range Query. Range Queries can be inclusive or exclusive of the upper and lower bounds. Sorting is done lexicographically.
mod_date:[20020101 TO 20030101]
Solr’s built-in field types are very convenient for performing range queries on numbers without requiring padding.
6. Launch the script
For this tutorial we will handle some apache logs with a splitText parser and send them to Elastiscearch Connect a shell to your logisland container to launch the following streaming jobs.
docker exec -i -t logisland-quickstarts_logisland_1 bin/logisland.sh --conf conf/core/match-queries.yml
7. Check the alert outputs
To see alert records flowing through kafka, run the following command :
sudo docker exec -ti logisland-quickstarts_kafka_1 /opt/kafka/bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh \\
--bootstrap-server kafka:9092 --topic logisland_alerts
You should see the apache log events such as :
@TODO put here a sample alert output
